DCS Protection for sudo vulnerability CVE-2021-3156
17231
03 February 2021
01 February 2021
CVE-2021-3156 refers to a critical heap buffer overflow vulnerability in Sudo, an open source cmdline utility that is widely available on several Linux distributions. The vulnerability can be exploited to achieve privilege escalation for a rogue non-admin user to gain root access and take over the host. Sudo is used to grant administrative control to selected trusted users defined in the sudoers list to run privileged commands on a temporary basis. However, exploiting CVE-2021-3156 allows any local unprivileged user to gain root-level access on a vulnerable host with default configuration bypassing any authorization checks.
The Qualys team that discovered the vulnerability demonstrated an exploit variant on an Ubuntu Linux server resulting in a root shell with full privileges on the server. The local user does not have to be an authorized sudoer. Several Linux distributions immediately released patches to resolve the vulnerability.
Details of the vulnerability are widely published, see the references below. The issue lies in the processing of the command line arguments when sudo is invoked in special modes, using the -s or -i options.
On a vulnerable system, running the below command as a non-admin user will trigger a buffer overflow, resulting in a segmentation fault.
sudoedit -s '\' `perl -e 'print "A" x 65536'`
DCS Protection:
DCS Prevention technology can protect against exploitation of the sudo vulnerability.
Add the following application rule in the DCS Unix prevention policy to prevent sudo from executing when invoked with suspicious arguments from CVE 2021-3156.
Policy Home-Application Rules-Add-Application
Application Name=SUDO-CVE-2021-3156
Add Program:
Program Path = *\sudo
Arguments = * *\\ *
Rule Name = SUDO-CVE-2021-3156
Configure the sandbox for the newly created application rule SUDO-CVE-2021-3156
Sandbox = Deny Sandbox
Prevention Policy configuration example:
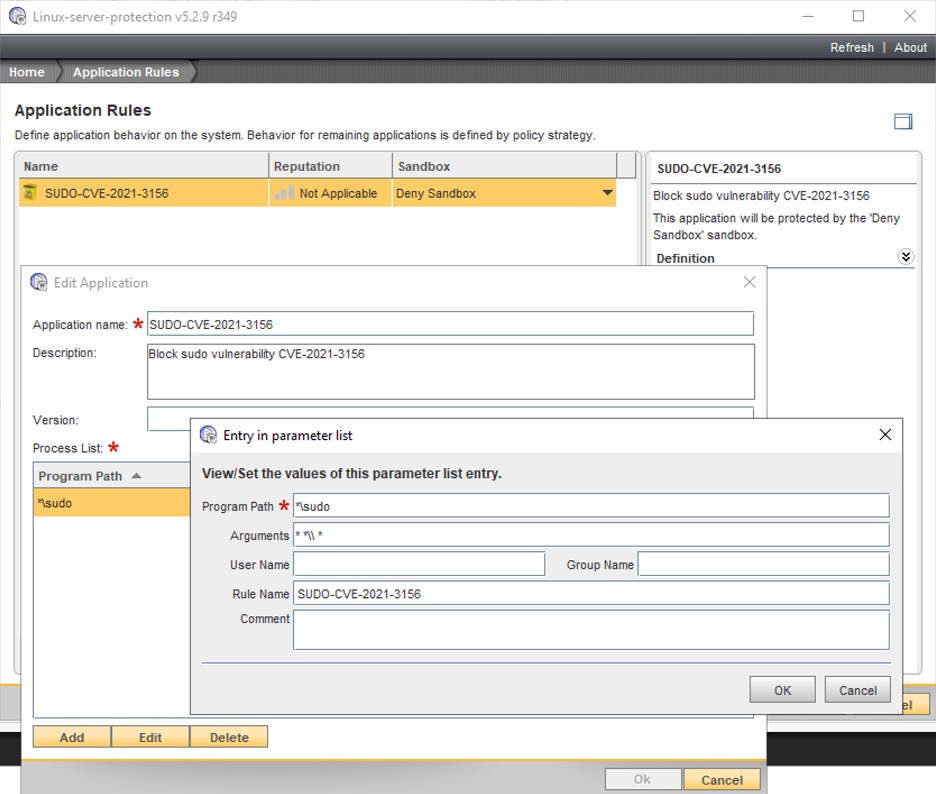
DCS out of the box Unix prevention policy provides default hardening of the root account which can be configured further to provide complete lockdown.
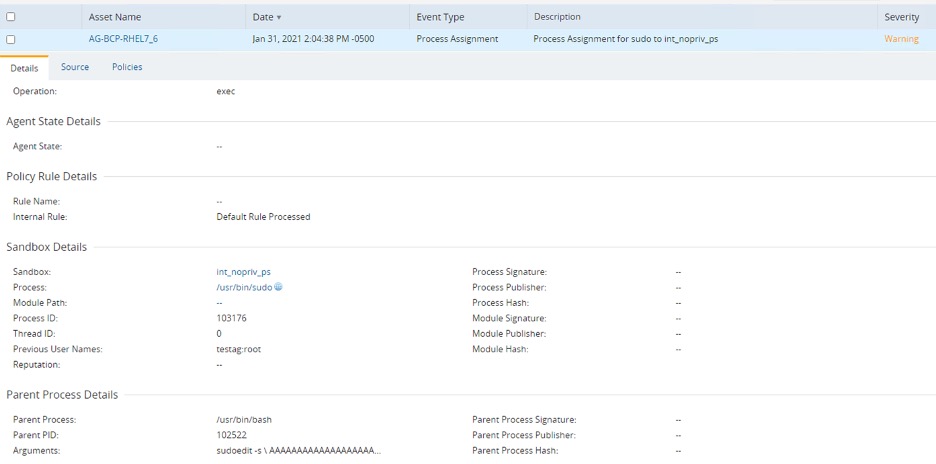
Sample DCS process assignment event in the Admin Console shows sudo program sandboxed with no DCS privileges and thus unable to execute. The event also captures the suspicious command line arguments used by the process.
DCS administrators can create an email alert notifying them of this suspicious activity on their servers.
DCS Detection:
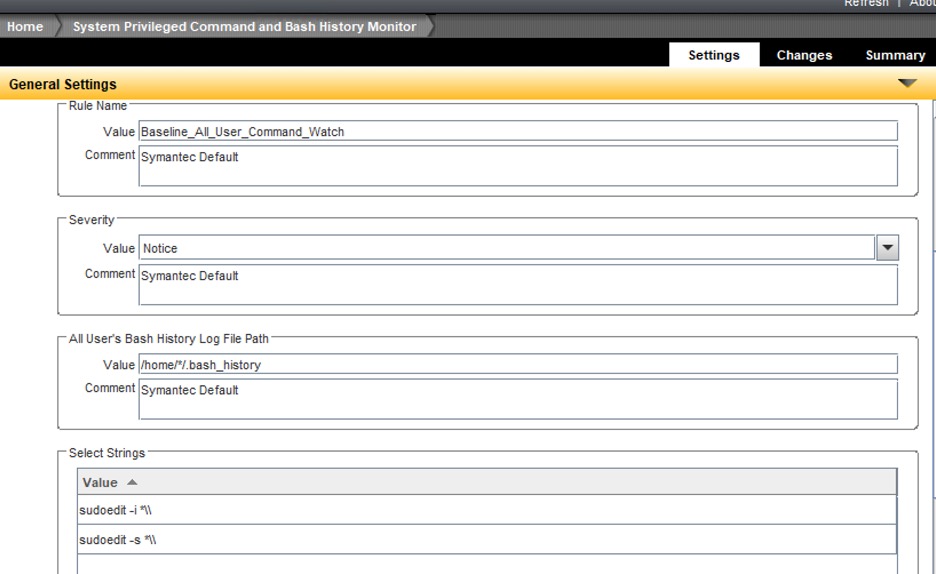
DCS Monitoring edition customers can enable System bash history monitoring in the Unix baseline detection policy to detect sudo usage with suspicious arguments.
Note the default entry under select string for All User's command history monitor control is * which means when enabled it will detect all commands including sudoedit logged to the user's bash history.
This can be configured as needed on the monitoring use cases.
Sample DCS detection rule monitoring suspicious sudo execution to trigger the buffer overflow vulnerability :
DCS detection event reported in the Admin Console when sudoedit is run to trigger CVE-2021-3156 buffer overflow vulnerability :
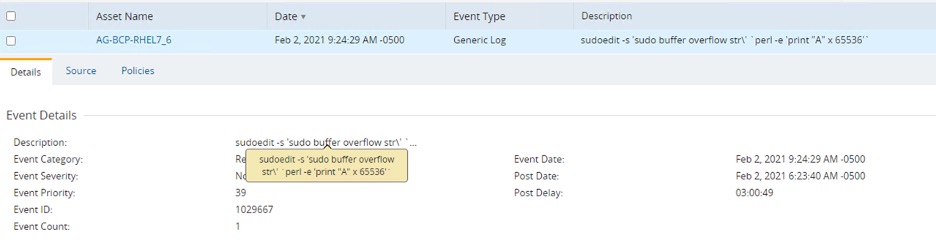
DCS administrators can create an email alert notifying them of sudo suspicious activity on their servers.
References:
https://www.sudo.ws/alerts/unescape_overflow.html